Use of Antibiotics for Ear Infections
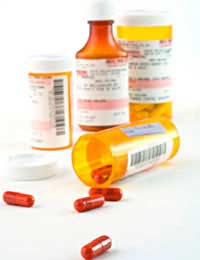
What Are Anti-Biotics?
Anti-biotics are a type of medication used to kill infections. They are only useful when targeting bacterial infections and will not work against viral infections.They are medications developed to help reduce and eliminate the continuation and spread of bacterial infections.They are normally available in tablet liquid, eardrop or intra-venous (administered directly into the blood stream) preparations and the doctor will prescribe specific doses of an appropriate route for each patient.Often, the first choice of an anti-biotics, by the physician will be what’s known as a ‘broad-spectrum’ anti-biotics, which can be used for general infections of many sources. If the infections continues after the treatment has ended, a swab of the infected area may be taken and sent for culturing, whereby the infections is grown under controlled circumstances in a laboratory so as to find out which specific anti-biotic will effectively destroy the bacterial cells.Normally, in the treatment of an ear infection, Augmentin or Amoxicillin will be prescribed as these are often the cheapest and most effective drugs for this complaint.
Indications For Use
Since their development, anti-biotics have proved very useful in eliminating illness and disease caused by bacteria. In modern society however, perhaps because of their continued use when not particularly necessary, they are becoming useless in the fight against some infections known as super-bugs. Due to this, their role in treating ear infections has become significantly reduced. Patients and parents alike are now advised only to seek medical advice with the possibility of using anti-biotic medication in the treatment of ear infections, if the infections is persistent and hasn’t improved by itself after 72 hours.Most physicians now agree that anti-biotics have been over prescribed in the past and are of the same opinion that most will heal themselves. More often than not, an ear infection will resolve itself using the body’s own immune system and pain relief, with symptoms beginning to subside between 48 and 72 hours after onset.Parents should seek medical advice if a child’s temperature continues to climb even after the use of paracetamol, or if a rash, bleeding or discharge appears.
For the treatment of persistent infections, anti-biotics are normally very successful in eradicating all bacterial infection as long as the full course of prescribed is taken. They are useful in the prevention of the spread of infection, particularly concerning the spread of ear infections to the brain or bones which are much more difficult to treat.
Side-Effects Of Taking Anti-Biotics
For many people, anti-biotic therapy can produce some unpleasant side effects including diarrhoea, oral thrush or a skin reaction. These are acceptable side effects and not normally considered to be a true allergy of the medication. Allergic reactions can cause swelling, vomiting or more seriously an anaphylactic response. If the airways become swollen, breathing becomes difficult or the hands and face begin to swell, discontinue the medication immediately and seek medical advice.Anti-biotics, if used sensibly and only when really needed are a fantastic way of treating bacterial infections. Always remember to take the full course prescribed even if symptoms have cleared up.
- Ear Injections for Meniere's Disease
- Glomus Tumours: Causes, Symptoms and Treatments
- How Does a Cochlear Implant Work?
- Types of Ear Surgery
- Drugs to Prevent Noise-induced Hearing Loss
- Can Music Help Tinnitus?
- What is an Ototoxic Drug?
- What is Auricular (ear) Acupuncture
- What to Expect from Ear Surgery
- Tinnitus Maskers
- Otoplasty or Pinning Back of the Ears
- Myringotomy
- Myringoplasty
- Ear Candling for Reducing Ear Wax Build Up
- Ear Drops and Their Uses
- Grommets and Your Ear

Re: Types of Ear Surgery
My child is born with deaf. So what should i do. Which treatment should i take to my child
Re: How Your Genes Shape Your Ear Lobes
My 2 month old has one free earlobe and his other ear has a half attached earlobe why? Should I be concerned?
Re: I Feel Dizzy and My Ear Itches: What Does it Mean?
I have noticed my ears are producing more sticky staff, itching and in the middle of last year I…
Re: Can Ear Wax Be Removed by Vacuum?
Vacuuming caused a 30% hearing loss. Don't allow it. Find a dr or audiologist who avoids it.
Re: Cysts and Tumours in the Ear
I had a pollock in my ear. can they regrow ?
Re: Grommets and Your Ear
@Ella - I'm afraid we can't give direct medical advice. The best option you have is to visit your GP and hope he/she will be able to help…
Re: Grommets and Your Ear
I had grommets when I was 2 and 5, a few weeks ago I found out I have scarring and 1 of my grommets are still in my ear meaning I had it in…
Re: Can Ear Wax Be Removed by Vacuum?
I had an ear wax removal procedure done at the Loma Linda, Ca Va facility. When the tech was vacuuming out the wax in my…
Re: Cysts and Tumours in the Ear
@CarrolA - I have no knowledge of your condition or what it might be. But if you want a quicker appointment, and peace of mind,…
Re: Cysts and Tumours in the Ear
I woke up one morning about five weeks ago with a feeling that my ear was blocked. A strange additional symptom is that every word…